What Is Business Messaging?
Business messaging refers to brands engaging in two-way conversations with customers and internal teams across various digital channels like SMS, WhatsApp, and Telegram. It enables personalized customer experiences, customer support, and simplified team collaboration by offering convenient, asynchronous communication and leveraging tools like AI chatbots for efficiency.
How business messaging works:
- Customer-initiated conversations: Customers can start a conversation with a brand from places WhatsApp, Telegram, or SMS.
- Asynchronous communication: This allows customers to message a brand at their convenience and return to the conversation later, avoiding the need to wait on hold.
- Multi-channel presence: Businesses can use tools and platforms to manage conversations across different messaging channels from a central location.
- Outbound messaging: Businesses can initiate messages to reach customers directly, often via integrated messaging platforms.
- AI and automation: Chatbots and automated responses can handle common questions and tasks, providing instant, scalable support and freeing up live agents for more complex issues.
- Integration with business tools: Business messaging platforms often integrate with CRM systems and other tools to create a more unified workflow and provide data-driven insights.
Main uses of business messaging include:
- Customer support: Brands use messaging to answer customer questions about products, store hours, or order status.
- Product discovery: Customers can browse styles or check product availability directly through a brand’s messaging interface.
- Proactive notifications: Businesses can send SMS messages for appointment reminders or other important customer notifications
Benefits of Business Messaging
Business messaging offers tangible advantages that enhance both customer experience and operational efficiency. By leveraging digital channels that people already use daily, businesses can create faster, more relevant, and effective communication.
- Higher engagement rates: Messaging platforms tend to have higher open and response rates than email or phone calls, leading to better customer interaction.
- Real-time communication: Businesses can respond instantly to customer queries, send immediate alerts, and manage time-sensitive conversations efficiently.
- Improved customer experience: Two-way messaging allows for more personalized and interactive conversations, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Cost efficiency: Automated workflows and chatbots reduce the need for large support teams, cutting down on operational costs while scaling service delivery.
- Integration: APIs allow messaging platforms to connect with CRM systems, order management tools, and help desks, centralizing communication and enabling better tracking.
- Channel flexibility: Businesses can reach customers through multiple platforms, such as SMS, WhatsApp, adapting to user preferences without building separate systems.
- Enhanced conversion rates: Timely, contextual messages can guide users through funnels more effectively, improving conversion metrics across sales and support.
- Global reach with local presence: Messaging apps like WhatsApp or SMS allow businesses to reach global users while maintaining local familiarity and trust.
How Modern Business Messaging Works
Here are the key elements of modern business messaging systems.
Customer-Initiated Conversations
Business messaging makes it possible for users to reach out on digital channels when they have questions, need support, or are interested in making a purchase. When a customer sends a message via SMS, email, or messaging app, it enters the business’s communication platform, where automated systems or live agents receive and respond. This immediacy helps set accurate expectations for resolution times and enables businesses to handle requests as they arise.
The benefit of customer-initiated messaging is that it places control in the hands of the consumer, who can escalate simple queries to more complex concerns as needed. This direct engagement fosters trust and reduces the friction often found in traditional customer service. Organizations can also use these interactions to gather data on commonly reported issues, helping improve future service delivery and product design.
Asynchronous Communication
One of the defining features of business messaging is its asynchronous nature, allowing conversations to pause and resume without requiring both parties to be present at all times. Messages are delivered instantly but can be read and responded to at the recipient’s convenience. This removes the pressure for customers and agents to respond in real time and accommodates different time zones and schedules.
For businesses, asynchronous communication offers the flexibility to handle large volumes of requests efficiently, even during peak periods. Agents or automated workflows can manage several open tickets in parallel, increasing responsiveness and reducing customer wait times. This approach leads to more thoughtful interactions and fewer errors compared to the rushed exchanges that frequently occur in synchronous channels like phone calls.
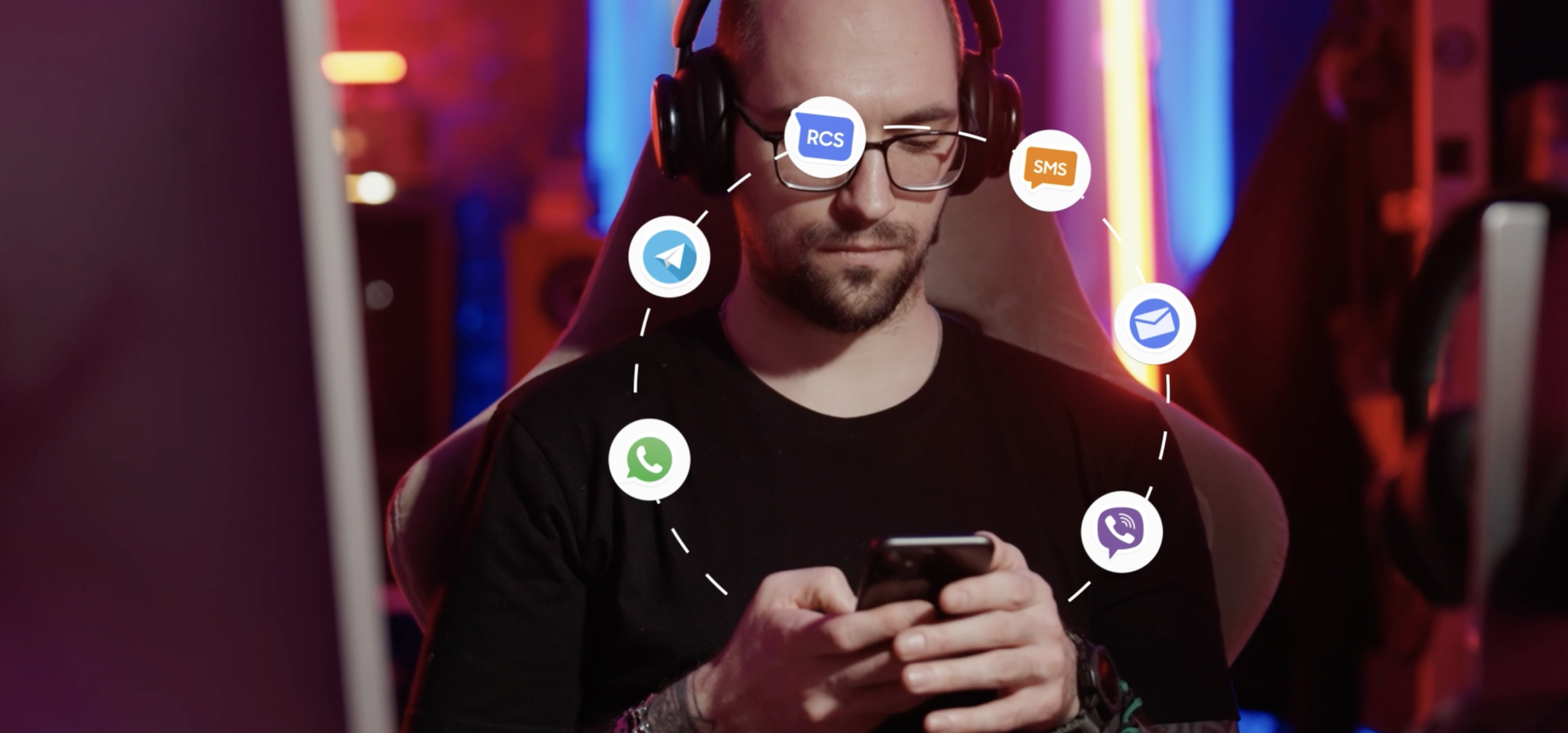
Multi-Channel Presence
A business messaging strategy supports a presence across multiple channels, including SMS, WhatsApp, Telegram, and email. By meeting customers on their preferred platforms, businesses remove friction and make engagement seamless. An integrated messaging solution ensures consistency, even as interactions shift across channels.
For organizations, multi-channel presence enables a single source of truth for all communications, simplifying workflows and making it easier to track conversations across different touchpoints. It also enhances brand reliability, as businesses appear accessible and responsive regardless of a customer’s chosen method. With APIs and routing rules, messages can be routed automatically to the right department or agent, preserving context throughout the journey.
Outbound Messaging
Outbound messaging refers to messages initiated by businesses to reach customers proactively. These messages can serve a variety of purposes, such as sending promotions, appointment reminders, billing notices, product updates, or service alerts. Outbound campaigns are often automated and scheduled through messaging platforms integrated with business systems, enabling precise targeting and timely delivery.
Effective outbound messaging strategies rely on consent-based audience segmentation, message personalization, and channel optimization. Businesses must consider the appropriate tone, timing, and frequency to avoid spamming recipients. With the right balance, outbound messaging improves engagement, reduces no-shows or delays, and keeps customers informed throughout their lifecycle.
AI and Automation
AI and automation elevate business messaging by handling routine queries, qualifying leads, and resolving common issues without human intervention. Chatbots powered by generative AI can guide users through troubleshooting, order status checks, or appointment scheduling, while escalating more complex queries to human agents.
For businesses, automation helps scale service capabilities, reduces human workload, and maintains responsiveness during off-hours. Automated responses manage common requests efficiently, freeing customer support reps to focus on complex tasks.
Integration with Business Tools
Modern business messaging platforms offer integration with CRM systems, ticketing software, payment gateways, and analytics tools to create a unified workflow. Incoming messages can trigger updates in backend systems, automatically open support tickets, or initiate personalized marketing campaigns. These integrations reduce manual tasks and ensure that agents have access to customer context within the flow of conversation.
Integration also allows businesses to track communication outcomes, measure campaign effectiveness, and automate regulatory compliance checks. By ensuring all systems are connected, organizations can deliver context-rich messaging experiences that improve both customer outcomes and internal efficiency.
What is Omnichannel Business Messaging?
Omnichannel business messaging refers to a unified communication strategy that allows businesses to interact with customers across multiple messaging channels while maintaining a consistent and continuous conversation experience. Unlike multichannel approaches, where each channel operates in isolation, omnichannel messaging ensures that all interactions are connected and contextual, regardless of the platform used.
For example, a customer may start a support conversation on WhatsApp, follow up via email, and receive a confirmation through SMS, all without losing the thread of the interaction. The conversation history, preferences, and context follow the user, enabling agents and automated systems to deliver coherent and personalized responses.
This approach improves customer satisfaction by eliminating the need to repeat information or restart interactions. It also allows businesses to manage communication more effectively through a single platform, routing inquiries intelligently and maintaining visibility across all channels.
Common Omnichannel Messaging Channels
SMS
SMS remains one of the most universally accessible messaging channels, working on virtually all mobile phones without the need for an internet connection. It’s suitable for time-sensitive alerts, authentication codes, and transactional updates.
In an omnichannel strategy, SMS serves as a reliable fallback channel, ensuring message delivery even when users are offline or not using app-based platforms. Its simplicity and reach make it critical for industries like banking, hospitality, and healthcare.
RCS
Rich Communication Services (RCS) is the next-generation upgrade to SMS, offering enhanced features such as read receipts, high-resolution images, and interactive buttons within the native messaging app on Android and Apple devices.
RCS enables brands to deliver app-like experiences without requiring additional downloads. For omnichannel messaging, RCS combines the ubiquity of SMS with the interactivity of chat apps, allowing businesses to engage customers with rich, personalized content directly in their default messaging interface.
Email remains a core component of omnichannel messaging, especially for transactional updates, account-related notifications, and longer-form communications. While not as immediate as chat-based channels, it is widely adopted and offers reliable delivery across devices and regions.
Email integrates easily with CRM systems and marketing automation tools, allowing businesses to personalize content, segment audiences, and track engagement metrics. In an omnichannel context, email complements real-time channels by providing persistent records and follow-up opportunities after live interactions have ended.
WhatsApp is one of the most popular messaging apps globally, making it a powerful channel for real-time business communication. With its Business API, companies can send notifications, support messages, and marketing content within a secure and encrypted environment.
WhatsApp supports rich media, quick replies, and templates, allowing businesses to automate workflows while keeping interactions conversational. Its broad adoption across demographics makes it useful for reaching customers in both emerging and developed markets.
Telegram
Telegram is known for its speed, privacy features, and growing adoption among tech-savvy users. It offers public channels, groups, and bot integrations, making it useful for both broadcast messaging and interactive customer service.
Businesses can deploy Telegram bots to handle support queries, conduct surveys, or push notifications. In an omnichannel setup, Telegram enhances reach by covering user segments not active on mainstream platforms like WhatsApp or Facebook Messenger.
Viber
Viber provides messaging and voice services to a large global user base, particularly in Eastern Europe, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East. The Viber Business Messages API enables brands to send promotional content, transactional updates, and customer service messages.
Viber supports branded profiles, rich media formats, and click-to-chat options, making it suitable for customer engagement in regions where it is a preferred platform. It also offers delivery and read status tracking, helping businesses measure message performance.
Related content: Read our guide to SMS marketing automation
6 Use Cases of Omnichannel Business Messaging with Examples
1. Transactional and Operational Notifications
Omnichannel business messaging streamlines transactional communications like order confirmations, delivery updates, and account alerts across platforms customers already use. A unified platform ensures these time-sensitive messages are sent via the most effective channel (SMS for urgent delivery, email for records, or WhatsApp for convenience) while maintaining full context.
Omnichannel messaging example:
A clothing retailer sends an order confirmation via email, a shipping update through WhatsApp, and a delivery notification via SMS. The customer can reply to any of these messages and continue the conversation with support from the same thread, regardless of channel.
2. Promotional and Marketing Messages
Promotional messaging across multiple touchpoints helps maximize reach and engagement. With omnichannel business messaging, marketing campaigns can be executed with consistent branding and tailored content on each platform, while syncing customer responses and preferences across systems.
Omnichannel messaging example:
A fitness app launches a subscription promo. Customers receive an in-app notification, followed by a reminder on WhatsApp. If unopened, a follow-up SMS is sent. The campaign manager tracks all responses and conversions from a central analytics dashboard.
3. Customer Support
Omnichannel messaging ensures customers receive support on their preferred platform without losing context. Support agents can access unified conversation histories, regardless of whether the customer initially reached out via SMS, email, or messaging apps.
Omnichannel messaging example:
A bank customer starts a query about a credit card charge via the bank’s WhatsApp channel. The issue is escalated and followed up via email. Later, the customer confirms resolution over SMS. The entire interaction is logged in the CRM, with agents having full context at every touchpoint.
4. Product Discovery
Businesses can guide users through the consideration and selection process with real-time product recommendations, catalog browsing, and inventory checks delivered seamlessly across platforms.
Omnichannel messaging example:
A cosmetics brand allows users to browse its product catalog via WhatsApp, where a bot suggests items based on user preferences. The customer asks follow-up questions on Telegram and receives a personalized recommendation and purchase link. The full conversation history is synced across both channels.
5. Internal Team Communication
Omnichannel tools aren’t limited to customer-facing scenarios. Internal team coordination can also benefit, especially in distributed or hybrid work environments where different departments prefer different platforms.
Omnichannel messaging example:
A logistics company uses Viber for planning and dispatch, but drivers communicate via SMS and WhatsApp. The central messaging hub syncs updates, status changes, and alerts across all platforms, giving managers a complete view without forcing tool changes.
6. Proactive Notifications
Proactive engagement helps prevent issues, remind users of actions, and improve customer satisfaction. Omnichannel messaging enables timely delivery and follow-ups across devices and channels.
Omnichannel messaging example:
A dental clinic sends an appointment reminder via WhatsApp, a calendar invite through email, and a same-day SMS reminder. If the patient replies with a question on any platform, the clinic’s system routes it to the same support team with full context intact.
Challenges in Implementing Business Messaging
Managing Multiple Channels and APIs
Supporting customers across SMS, WhatsApp, Messenger, email, and other platforms requires managing numerous APIs and integration endpoints. Each channel may have its own technical requirements, rate limits, and compliance obligations. Keeping up with platform changes and coordinating updates is resource-intensive, especially for large-scale deployments.
How to overcome:
Using a communications platform as a service (CPaaS) helps streamline integration with multiple messaging channels by offering prebuilt connectors and unified APIs. CPaaS providers abstract the complexity of individual platforms, manage compliance, and handle message routing, reducing the need for in-house development and ongoing maintenance.
Consistency of Brand Voice Across Systems
With so many messaging channels and touchpoints, maintaining a consistent brand voice is a significant challenge. Each platform has unique tone, formatting, and length constraints, which can lead to fragmented experiences. Ensuring every message aligns with core brand guidelines takes coordination between marketing, support, and product teams.
How to overcome:
Establish centralized content libraries, tone-of-voice guidelines, and message templates that can be adapted to different channel constraints while maintaining consistent language and branding. Use shared style guides and enforce brand QA processes across marketing and support teams. Modern messaging platforms often include tools for previewing and standardizing content across channels.
Scaling Infrastructure for Global Reach
Delivering business messaging at a global scale requires infrastructure that supports diverse geographies, time zones, and languages. International expansion brings varying regulatory standards, telecom carrier rules, and message delivery limitations. Businesses need resilient platforms that maintain uptime, quickly adapt to local requirements, and provide multi-language support.
How to overcome:
Adopt cloud-native messaging platforms with regional data centers, multi-language capabilities, and built-in compliance features for international markets. Choose vendors that offer intelligent routing, localized delivery optimization, and SLA-backed uptime guarantees. Leverage translation services and schedule-aware automation to support customers in their own language and timezone while ensuring reliability at scale.
Integration with Legacy Environments
Many businesses rely on legacy systems that lack out-of-the-box support for modern messaging APIs or automation platforms. Integrating new messaging solutions with older CRM, ERP, or ticketing tools can require complex middleware and custom development. This increases project timelines and often demands ongoing maintenance and support.
How to overcome:
Deploy middleware platforms or integration tools that bridge modern APIs with older systems. Low-code or no-code integration layers can connect business messaging platforms to legacy CRMs and ERPs without major refactoring. Businesses can also adopt modular architectures, enabling phased upgrades and parallel operation with existing tools during the transition period to reduce disruption and simplify long-term maintenance.
Key Features of Business Messaging Solutions
Modern business messaging solutions are built with capabilities to simplify communication, support automation, and ensure reliability across channels. These features enable businesses to manage high message volumes while maintaining quality and responsiveness.
- Unified messaging inbox: A centralized dashboard aggregates messages from all supported channels (such as SMS, WhatsApp, email, in-app chat) into a single interface. This helps agents manage conversations efficiently without switching between tools.
- Automated workflows and chatbots: Predefined flows and AI-powered bots handle routine queries, lead qualification, appointment booking, and order tracking, reducing manual workload and improving response speed.
- Message routing and escalation rules: Intelligent routing sends incoming messages to the most appropriate agent or team based on criteria like language, topic, or customer profile. Escalation paths are also defined to handle unresolved or complex queries.
- APIs for system integration: Open APIs allow integration with CRMs, ERPs, payment systems, analytics tools, and more, enabling real-time data exchange and workflow automation.
- Analytics and reporting: Built-in dashboards provide insights into key metrics such as message delivery rates, response times, open rates, and agent productivity.
- Multi-language support: Language detection and translation features ensure messages can be automatically translated, enabling businesses to serve global audiences effectively.
- Consent and compliance management: Tools to manage opt-ins, unsubscribe requests, and audit logs help ensure adherence to regulations like GDPR, TCPA, and local telecom rules.
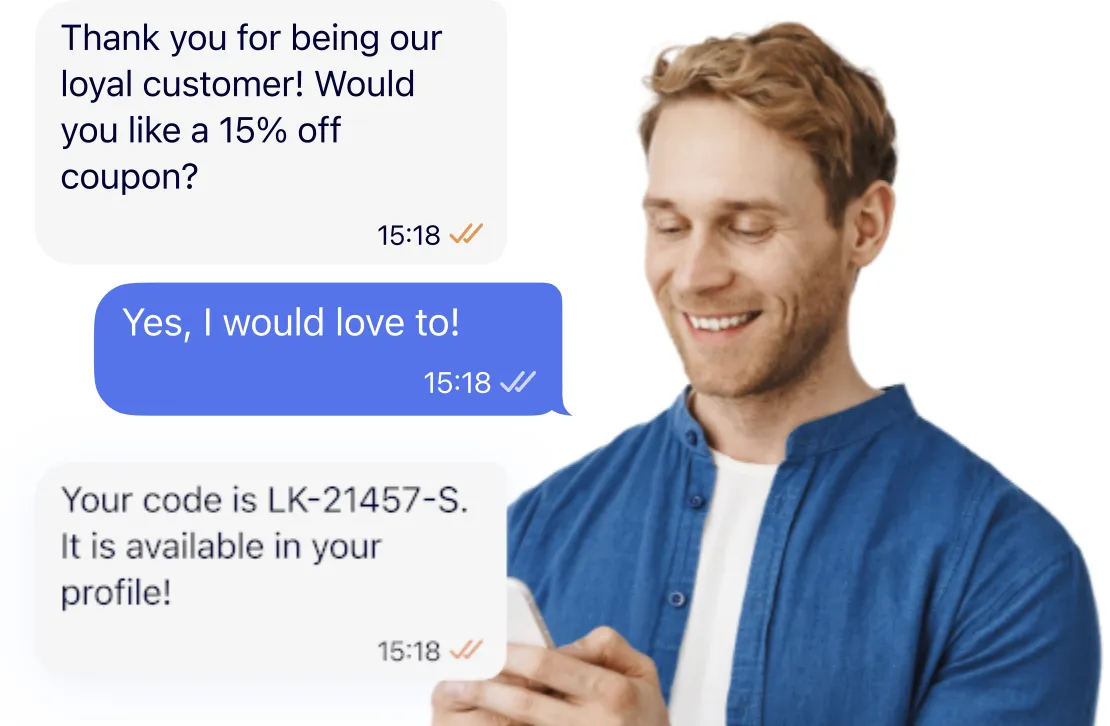
- Message templates and personalization: Pre-approved templates speed up communication while dynamic fields allow personalization based on customer data, improving engagement.
- Role-based access and permissions: Granular controls define who can view, edit, or send messages, supporting operational security and role-specific workflows.
- Failover and delivery optimization: Systems are designed for high availability and include failover mechanisms to ensure message delivery even during outages or peak loads.
Best Practices for Business Messaging Success
Here are a few best practices that can help your organization effectively implement business messaging solutions.
1. Ensure Clear Opt-In and Compliance Workflows
Obtaining explicit opt-in for business messaging is essential, not only to comply with regulations such as GDPR and TCPA but also to build customer trust. Consent workflows should be simple, transparent, and clearly communicate the type and frequency of messages recipients will receive. Maintaining clear audit trails and providing easy opt-out mechanisms keep businesses compliant and demonstrate respect for user preferences.
Rigorous consent management reduces legal risk and helps prevent unwanted communication that could damage brand reputation. Automated systems can flag non-compliant data or high opt-out churn, enabling teams to adapt tactics and preserve deliverability. Regularly reviewing and updating compliance workflows in response to changing regulations keeps organizations ahead of legal challenges.
2. Personalize Without Overstepping Privacy Limits
Personalization is vital for engagement but must stay within customers’ privacy expectations and legal boundaries. Collect only the data necessary for delivering relevant, timely content, and ensure transparency about its use. Allow users to set preferences and manage their own data, combining automation with customer control.
Businesses should adopt privacy-by-design principles and adhere to data minimization standards. Algorithms should avoid sensitive inferences and ensure that personalized messages do not feel invasive or inappropriate. Regular audits, privacy policies, and clear data-handling disclosures not only protect the business but also build long-term trust.
3. Use Automation Intelligently to Enhance, Not Replace, Humans
Automation simplifies responses to routine requests, but complex or sensitive issues are best handled by skilled agents. Design workflows to detect intent and escalate to human support when needed, preserving empathy and context in challenging scenarios. Well-balanced systems create smooth transitions between chatbots and people, minimizing customer frustration.
Intelligent use of automation also involves continuous monitoring and improvement of bot performance. Collect feedback, review unresolved cases, and adjust conversational flows accordingly. Automation should free human resources for high-value work.
4. Maintain Consistent Tone and Formatting Across Channels
Customers value reliability in brand communication, regardless of where the interaction takes place. To ensure consistency, create standardized templates, glossaries, and personalization tokens that apply across SMS, messaging apps, and email. Synchronize updates to brand voice guidelines and use specialized tools to preview messages as they appear on each platform.
Automate formatting checks and run regular quality audits on outbound content. Train agents and content creators on brand standards and monitor multi-channel metrics for discrepancies in tone, length, or style. Consistency reinforces brand identity and helps customers trust that they’re interacting with the same organization on every channel.
5. Continuously Monitor Delivery Metrics and Response Analytics
Ongoing measurement is crucial to optimize business messaging performance. Track key metrics such as delivery rates, open/read rates, and response times to identify strong and weak points in messaging strategies. Use analytics dashboards for real-time insights and long-term trends, adjusting tactics based on evidence rather than assumptions.
Analyze bounce rates, opt-out patterns, and response paths to isolate technical or engagement issues. A/B testing can refine copy, timing, and workflows for maximum effect. Applying findings from regular reporting ensures business messaging stays relevant, effective, and aligned with organizational goals.
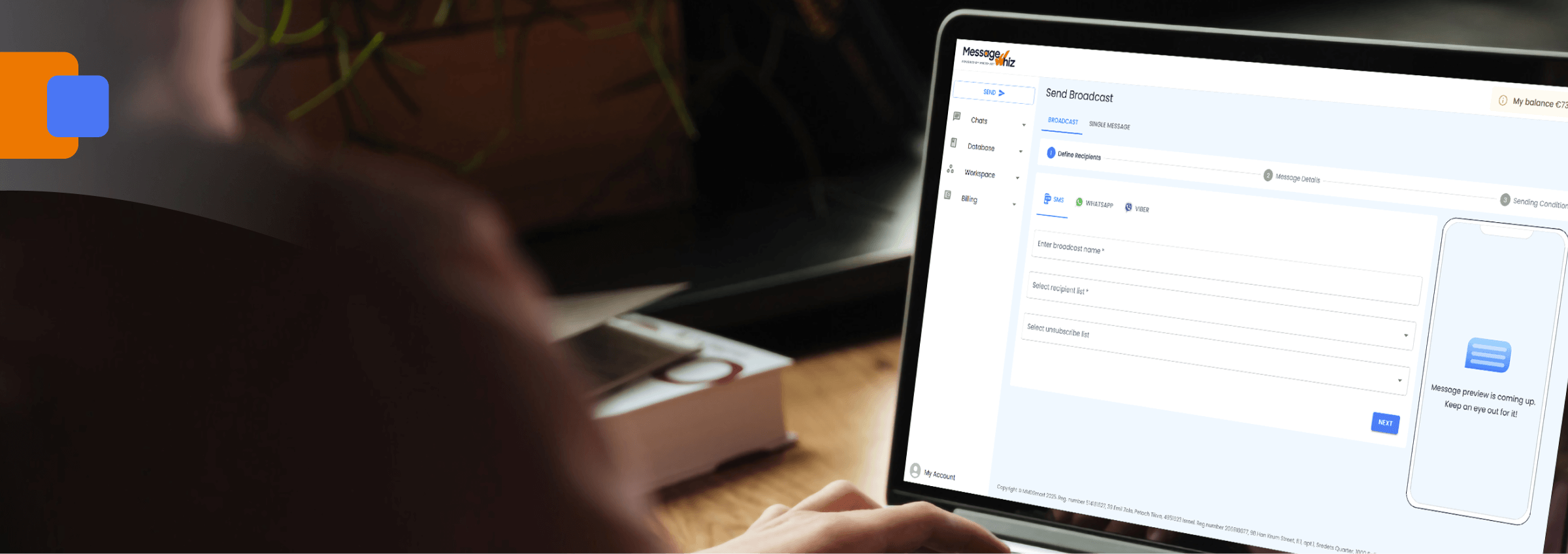
Omnichannel Business Messaging with MessageWhiz
MessageWhiz’s CPaaS platform brings true omnichannel communication to life, helping businesses connect with customers across SMS, WhatsApp, RCS, email, and voice from a single unified platform. Instead of managing each channel separately, MessageWhiz allows every interaction to flow seamlessly, ensuring customers enjoy a consistent and contextual experience no matter where the conversation starts or continues.
With MessageWhiz, marketers and customer service teams can easily design, automate, and personalize campaigns that follow the customer journey across multiple touchpoints. Whether confirming a booking on WhatsApp, sending an OTP by SMS, or delivering an upsell via email, all messages are coordinated through a central dashboard for real-time insights and performance tracking.
Built for scalability and security, MessageWhiz integrates with leading CRMs and marketing automation tools, empowering financial services, gaming, travel, and eCommerce brands to maximize engagement and conversions while maintaining compliance and deliverability.






























![10 SMS Marketing Services Compared [2026 Guide] | Message Whiz blog image](https://messagewhiz.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/smiling-woman-holding-smartphone-remixed-media-2.jpg)
