What Are OTP Services?
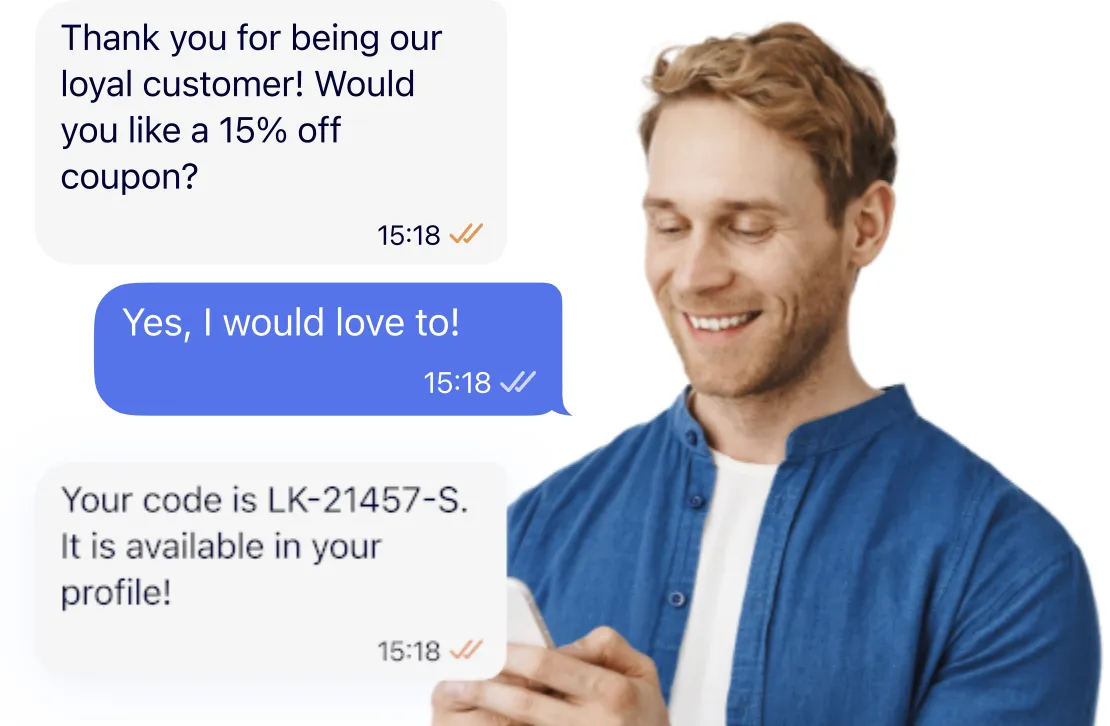
OTP (one-time password) services provide a mechanism for verifying user identity by generating and transmitting a temporary, unique code for authentication. These services are widely used in online banking, eCommerce, and enterprise systems to add an extra layer of security beyond traditional static passwords.
OTPs are typically valid for a short period and can be used only once, minimizing the window of opportunity for malicious actors to compromise an account. The code can be delivered using various channels such as SMS, email, dedicated mobile applications, or physical devices.
The primary goal of OTP services is to prevent unauthorized access, particularly from attackers who might possess stolen passwords or other login credentials. By requiring the user to present a one-time, time-bound code along with their regular login details, OTP systems significantly raise the difficulty of unauthorized entry.
Types of OTP Services
SMS-Based OTP Services
SMS-based OTP services send one-time passwords to users via text messages sent to their registered mobile number. This approach has become widespread due to the ubiquity of mobile phones and the simplicity of SMS technology. SMS OTPs are easy for users to access and require no additional device setup or app installation, making them convenient for both end users and service providers. The infrastructure leverages existing telecom networks and works well even on basic feature phones.
However, SMS OTP services face several security and reliability challenges. Attackers can intercept messages through SIM swapping, number porting fraud, or ss7 protocol vulnerabilities. Delays in message delivery can also disrupt authentication, particularly when users travel internationally or encounter network congestion. Despite these concerns, SMS OTPs remain prevalent due to their ease of use and broad coverage, especially in markets with limited smartphone adoption.
Email-Based OTP Services
Email-based OTP services deliver one-time codes through emails sent to the user’s registered email address. This method relies on the assumption that the user’s email account is secure and accessible. Many organizations use email OTPs as a backup or secondary authentication method when SMS or app-based methods are unavailable. The process is straightforward and requires users only to have access to their usual email inbox via webmail or client.
Security considerations are important with email-based OTPs, as the risk of email account compromise or phishing attacks is significant. OTP emails may be delayed or diverted to spam folders, impacting the timeliness and reliability of delivery. Strong email hygiene, domain reputability, and anti-phishing training for users are essential when deploying email OTPs. Despite these factors, email OTPs remain integral in environments where SMS or hardware/app tokens are impractical.
Messaging App OTP Services
Messaging app OTP services use encrypted messaging platforms such as WhatsApp, Telegram, or Signal to deliver one-time passwords directly to users. These platforms offer an alternative to traditional SMS by leveraging internet-based messaging, which can be more reliable and secure, especially in regions with poor cellular service or high SMS interception risks.
This approach benefits from the end-to-end encryption and identity verification mechanisms provided by modern messaging apps. Delivery is often faster than SMS, and users are more likely to engage with messages in apps they actively use. Some service providers integrate OTP workflows directly with messaging APIs, allowing automated, scalable delivery through official business accounts.
Security risks include potential account takeover of the messaging app itself, particularly if the user’s device lacks proper lock screen protection or if backup methods are insecure. Additionally, OTPs in messaging apps can be exposed if notifications are displayed on unlocked screens. Despite these concerns, messaging app OTPs are gaining traction, particularly in regions where these apps are the dominant communication method.
App or Software Token (Time-Based) OTP Services
App or software token OTP services use applications installed on smartphones or computers to generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTP). Popular apps like Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, and Authy generate codes locally on the device, synchronized using a shared secret and the current time. Since generation happens client-side and doesn’t require internet or cellular connectivity after the initial setup, these apps offer strong reliability and security.
The primary advantage of app-based OTPs is their resilience to phishing and interception attacks targeting external delivery channels (such as SMS or email). Codes can’t be intercepted during transmission, and device access is typically protected by biometric or passcode authentication. However, initial onboarding can be complex for non-technical users, and device loss can lock users out unless backup and recovery options are in place. Nonetheless, app-generated OTPs are now standard in corporate, financial, and personal security ecosystems due to their security profile and ease of scaling.
Hardware Token / Physical OTP Device Services
Hardware token OTP services involve dedicated physical devices, often key fob-sized gadgets, that generate OTPs at regular intervals. Each device uses a unique cryptographic key shared with the authentication server. Hardware tokens are recognized for their security, as they operate offline and are immune to malware or remote attacks targeting phones or computers. Banks and enterprises have used hardware OTPs for decades, particularly for employee and customer authentication.
Despite strong security, hardware tokens bring logistical challenges. Distribution, inventory tracking, and replacement management add operational overhead. Users must carry the device and ensure it is available when needed, which can create friction compared to software-based solutions. Device loss or malfunction can also be disruptive, necessitating efficient provisioning and emergency access procedures. As mobile-based alternatives have improved, hardware OTP devices are now more common in environments demanding high assurance, such as defense, finance, and critical infrastructure.
Notable OTP Services
1. MessageWhiz
![]()
MessageWhiz provides a high-reliability OTP service designed for security-sensitive and latency-critical authentication workflows. Built on operator-grade telecom infrastructure, MessageWhiz controls message routing end to end rather than relying solely on third-party aggregators. This enables faster delivery, higher completion rates, and more consistent OTP performance across regions—particularly in international and high-volume environments where delivery failures directly impact user conversion.
The platform supports OTP delivery across SMS, WhatsApp, voice calls, and email, allowing organizations to design multi-channel verification flows with intelligent fallback logic. AI is applied at the routing and monitoring layers to continuously optimize delivery paths and detect anomalies that could indicate congestion, fraud, or degraded routes. This makes MessageWhiz well suited for use cases such as account login, transaction confirmation, onboarding verification, and fraud prevention.
Key OTP capabilities include:
- Multi-channel OTP delivery: Send one-time passwords via SMS, WhatsApp, voice, or email, enabling flexible verification strategies based on user preference, region, or risk profile
- Operator-grade SMS routing and delivery control: Direct control over telecom routing paths as a transit operator, delivering higher OTP arrival rates and reduced latency compared to reseller-based OTP services
- AI-driven routing optimization: AI continuously evaluates delivery performance, congestion, and destination behavior to optimize OTP routing in real time
- Intelligent fallback and failover logic: Automatically switch channels or routes when delivery delays or failures are detected to maintain verification continuity
- Configurable OTP parameters: Control code length, expiration windows, retry limits, and resend logic to align with security policies and user experience requirements
- Real-time monitoring and analytics: Track OTP delivery success, latency, failure reasons, and regional performance through live dashboards and reporting
- Fraud and abuse mitigation support: Rate limiting, traffic monitoring, and anomaly detection help reduce exposure to SMS pumping, replay attempts, and verification abuse
- API-first integration: Simple APIs, webhooks, and event callbacks enable fast integration with authentication systems, identity platforms, and application workflows
Why MessageWhiz stands out among OTP service providers
While many OTP providers focus primarily on code generation and basic delivery, MessageWhiz differentiates by optimizing how OTPs actually reach users. By combining programmable verification workflows with direct telecom control and AI-driven delivery optimization, MessageWhiz helps organizations reduce login friction, improve verification success rates, and maintain security at scale—especially in global, high-growth environments.
2. Twilio Verify API

Twilio Verify API provides multi-channel user verification across SMS, email, WhatsApp, voice, and TOTP, along with optional silent network authentication for reduced-interaction verification. The service manages code generation, delivery routing, fraud controls, and regulatory variations across regions.
Key features include:
- Fraud protection: Uses Fraud Guard to block fraudulent SMS pumping attempts, applying automated detection and traffic filtering to prevent unauthorized verification requests.
- Phone number management: Procures and manages short codes, long codes, toll-free numbers, and global alpha-sender IDs to support regional delivery requirements and carrier constraints.
- Template handling: Provides carrier-approved message templates that auto-translate into multiple languages, reducing template rejection and improving delivery consistency across markets.
- Analytics and insight: Offers dashboards showing regional conversion rates, channel performance, and fraud trends to support operational monitoring and routing adjustments.
- Silent verification: Supports silent network authentication for device-based verification that avoids code entry and reduces user interaction in supported environments.
- Compliance posture: Supplies PII-less flows and holds HIPAA and SOC 2 Type 2 certifications to support regulated applications without requiring storage of identifiable user data.
3. MessageBird SMS OTP
![]()
MessageBird provides an SMS-based OTP service built on a licensed, carrier-grade network designed to support delivery across 150 countries. The service offers routing controls, number availability, and developer-oriented APIs intended to manage authentication workflows and adapt delivery behavior to regional conditions.
Key features include:
- Carrier-grade backbone: Operates as a licensed carrier to interconnect with mobile operators directly, aiming to support consistent OTP delivery characteristics across international regions and traffic patterns.
- Intelligent routing: Uses a proprietary routing algorithm that can be tuned for speed, quality, or cost while exposing real-time conversion data through a conversion API for monitoring and adjustments.
- Global numbering options: Provides access to local, national, toll-free, and phone numbers in more than 150 countries to align OTP sending with regional numbering requirements.
- Developer-oriented APIs: Offers auto-scaling APIs, documentation, and SDKs that support rapid integration and accommodate high-volume OTP workflows without extensive configuration overhead.
4. Sinch

Sinch offers an SMS-focused verification service that monitors route performance, prioritizes conversion-based routing, and provides APIs and SDKs for implementing OTP verification without managing operator connections, latency tracking, or regulatory requirements manually.
Key features include:
- Conversion-based routing: Selects SMS routes using conversion performance rather than delivery receipts, aiming to mitigate latency issues and reduce dependence on limited delivery indicators across networks.
- Real-time analytics: Provides analytics on conversion rates, route behavior, and fault patterns, enabling ongoing evaluation of verification performance without relying solely on delayed or incomplete delivery receipts.
- APIs and SDKs: Supplies REST APIs and SDKs designed to simplify verification setup, reducing engineering effort for building authentication workflows across mobile and web applications.
- Fallback management: Supports blending verification methods and managing fallback options to address delivery failures, helping maintain service continuity when SMS channels underperform regionally.
- Regulatory alignment: Offers built-in handling of regional telecom and compliance requirements, reducing the need for manual monitoring of regulatory changes in target markets.
- Multi-method verification: Provides additional verification types such as flash call, phone call, and data verification, expanding options beyond SMS and accommodating varied device or network conditions.
Source: Sinch
5. MSG91 OTP

MSG91 provides an OTP service that supports multiple delivery channels, built-in failover behavior, configurable integration components, and monitoring features for observing OTP performance.
Key features include:
- Multi-channel delivery: Sends OTPs through SMS, WhatsApp, email, and voice, selecting among channels to maintain delivery when network conditions or user accessibility vary across environments.
- Failover mechanism: Switches to an alternate delivery method when the primary channel cannot complete an OTP transmission, aiming to reduce delays and maintain consistent code availability.
- Plug and play integration: Provides an OTP widget and simplified setup steps that limit configuration work, enabling teams to embed verification without extensive code changes or custom workflows.
- Real-time analytics: Supplies reporting on delivery outcomes, channel performance, and user interaction patterns to support operational analysis and data-informed adjustments.
- Inbuilt IP security: Restricts OTP access to trusted IP ranges, adding a control layer that limits exposure of verification traffic and reduces unauthorized retrieval attempts.
6. Infobip OTP

Infobip provides an SMS OTP service that relies on direct operator connections, configurable verification settings, and fallback options to support authentication across global markets.
Key features include:
- Direct telco connections: Uses a large set of direct operator links to reduce delivery delays and support consistent OTP arrival times across regions with varying network quality.
- Security controls: Applies measures such as short code expiry and rate limiting while holding GDPR, ISO 27001, and SOC 2 compliance to manage security expectations for OTP traffic.
- Localized sender IDs: Supports branded sender identities tailored to local markets, helping align outbound OTP messages with regional norms and user recognition patterns.
- Fallback logic: Retries OTP delivery through alternate communication channels when the initial attempt fails, allowing verification flows to continue under adverse conditions.
- Configurable parameters: Allows adjustments to OTP code length, expiration windows, and retry behavior, enabling teams to match authentication settings to internal policies.
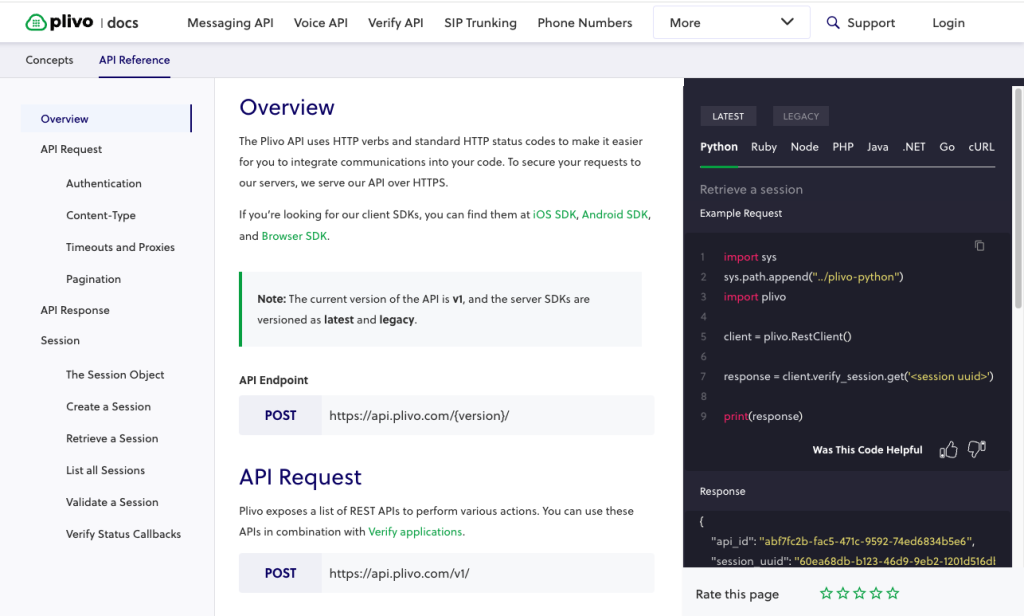
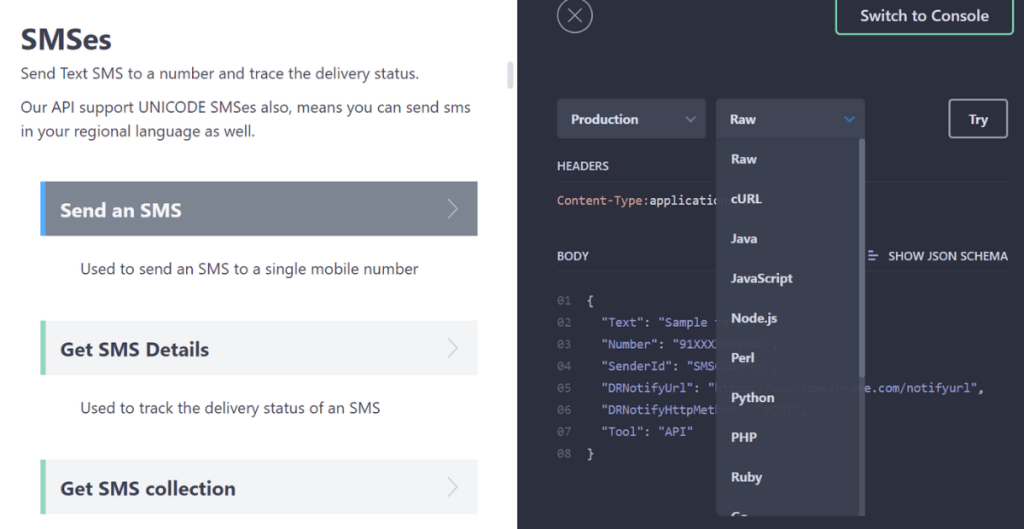
7. Plivo Verify API

Plivo Verify API supports creating, sending, and validating OTPs across SMS, voice, and WhatsApp while providing tools for regulatory alignment, fraud protection, and configuration management. The service also offers pre-registered sender IDs, templates, and developer-oriented APIs to accelerate deployment.
Key features include:
- Channel coverage: Sends OTPs over SMS, voice, and WhatsApp, with additional channels such as RCS and email referenced as upcoming options intended to expand delivery pathways.
- Fraud protection: Includes an AI-driven fraud shield designed to detect and block sms pumping activity, reducing unwanted traffic by applying automated screening to verification requests.
- Regulatory facilitation: Uses pre-registered sender IDs and templates in markets like the US, India, and the UK, helping bypass paperwork and simplify go-live steps for regulated regions.
- Developer tooling: Provides sample code, multi-language SDKs, and APIs to shorten implementation time, enabling creation and validation of verification sessions with minimal configuration.
- Template and language control: Allows management of OTP templates, language selection, and configuration adjustments without extensive code changes, supporting varied deployment needs.
8. SMSCountry

SMSCountry provides an OTP SMS service focused on rapid delivery, operational security, and integration flexibility.
Key features include:
- Common use cases: Supports identity verification and payment confirmation scenarios, reflecting typical triggers for sending OTPs during account creation or transaction approval.
- Premium routes: Uses premium SMS pathways intended to maintain consistent deliverability and reduce exposure to unreliable or congested message routes under varying traffic loads.
- Quick onboarding: Offers simplified activation steps that minimize initial configuration work, enabling faster access to sender settings, templates, and regional delivery options.
- Integration flexibility: Provides APIs and integration options designed to accommodate different systems and workflows without restricting developer environments.
9. TeleSign SMS Verify

TeleSign’s SMS verification service provides SMS-based one-time passcodes supported by direct-to-carrier connectivity, routing controls, and fraud-detection capabilities.
Key features include:
- Global coverage: Reaches users across a wide set of countries and languages, using direct connections to hundreds of carriers to support large-scale verification programs.
- Dynamic routing: Selects delivery paths based on current network conditions to reduce latency and maintain message continuity when individual routes degrade or fail.
- Waterfall delivery: Applies a fallback approach that shifts traffic to alternate routes or channels when primary delivery attempts do not complete successfully.
- Number insights: Uses phone-number intelligence to assess validity, reduce fake account creation, and improve the accuracy of verification-related risk models.
- Traffic monitoring: Flags anomalies in message volume or behavior and enables traffic segmentation to limit exposure to communication fraud or unexpected delivery failures.
- SIM swap detection: Checks recent SIM changes to identify potential account-takeover attempts and enforce verification rules based on carrier-reported status.
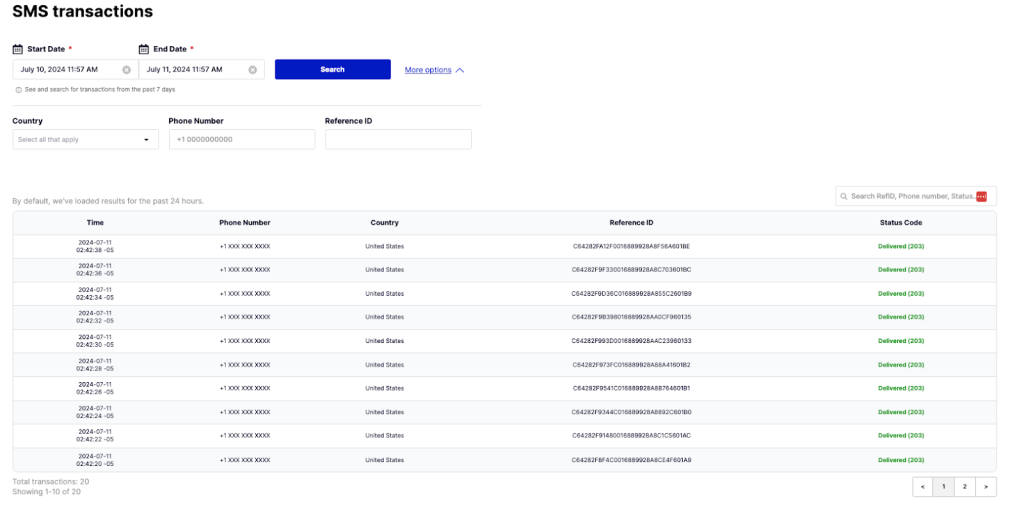
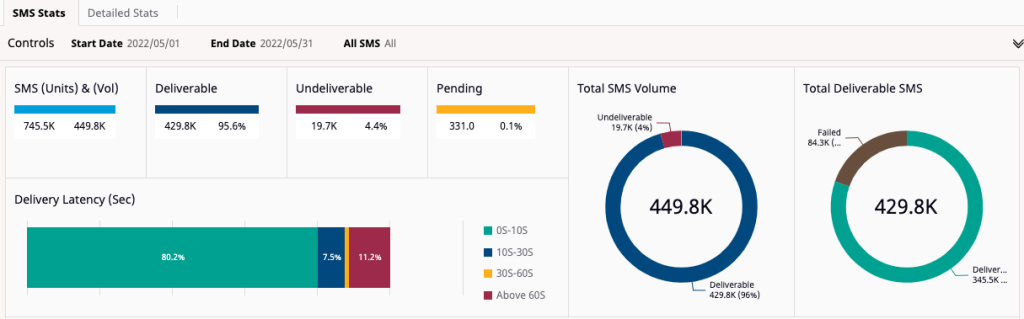
10. Exotel

Exotel provides SMS and voice-based OTP services that deliver verification codes, manage delivery through operator connections, and support reporting and basic configuration via APIs.
Key features include:
- SMS OTP delivery: Sends verification codes over SMS with stated attention to deliverability and latency, aiming to support time-sensitive authentication in varied network conditions.
- Voice OTP option: Places automated voice calls that play digit sequences for verification, offering an alternative when text delivery is limited or unavailable for certain users or regions.
- Support access: Provides customer support through multiple channels, including phone, email, and social platforms, with availability positioned for continuous assistance.
- Implementation path: Supplies REST APIs for integrating OTP delivery and enables account setup in short time frames, reducing initial configuration steps for basic verification workflows.
- Reporting features: Offers daily reporting that summarizes delivery and verification activity, allowing routine monitoring of OTP traffic and performance characteristics.
Choosing an OTP Service Provider
Selecting the right OTP service provider is crucial for maintaining secure, reliable, and user-friendly authentication. Beyond standard features like multi-channel delivery or global reach, there are several nuanced considerations that organizations should evaluate to ensure alignment with their security requirements, operational needs, and user base.
Delivery speed and consistency
- Assess median and worst-case OTP delivery times across channels and geographies. Reliable latency is vital for user experience and session security.
- Request provider benchmarks and test performance in target regions, especially for SMS and voice.
Route transparency and failover logic
- Understand whether the provider uses direct operator connections or aggregators and how routes are optimized or switched during failures.
- Look for configurable failover logic (e.g., SMS to email or WhatsApp) to ensure delivery under adverse conditions.
Security and abuse protection
- Evaluate protections against OTP abuse, such as SMS pumping or phishing. Features like rate-limiting, HMAC signing, sender ID whitelisting, and OTP length/pattern control matter.
- Confirm adherence to standards like TLS encryption, secure secret provisioning, and authentication logs.
Compliance and data residency
- Verify the provider’s support for data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) and the location of message processing or user data storage.
- For regulated industries, ensure audit trails, message retention policies, and opt-in management are in place.
Integration and developer experience
- Review API documentation, SDK availability, and configuration flexibility (e.g., template management, localization).
- Consider onboarding time, support for sandbox environments, and availability of webhook callbacks and delivery receipts.
Monitoring and observability
- Ensure real-time delivery reports, analytics dashboards, and alerting are available to track OTP success rates, latency, and anomalies.
- Observability is critical for debugging, SLA enforcement, and adapting to changes in delivery performance.
Cost structure and volume handling
- Examine per-message pricing across regions, volume discounts, and additional charges for templates, premium routes, or compliance features.
- Consider the provider’s scalability under peak loads and the impact of burst traffic on OTP performance.
Local regLocal Regulatory Readiness
- Some markets (e.g., India, UAE) impose telecom-specific compliance (e.g., DLT registration, template pre-approval). Ensure the provider is equipped to support such requirements.
Conclusion
OTP services strengthen authentication by adding time-bound, single-use checks that reduce the impact of stolen or reused passwords. Each delivery method carries trade-offs across reliability, security, user experience, and operational complexity, making multi-channel strategies common in modern systems. Selecting the right provider involves analyzing delivery performance, integration depth, compliance posture, and protections against abuse, enabling organizations to deploy OTP verification that is both secure and resilient at scale.